Inflation is baked into the cake
First, please read the Disclaimer.
Inflation is a hot topic at the moment. For good reason: higher inflation would drive up interest rates, affecting both bond and equity prices, as well as commodities and precious metals.
March CPI jumped to 2.64% but the increase is partly attributable to the low base from March 2020. Core CPI (excluding food and energy) came in at a more modest 1.65%. The main difference between CPI and core CPI is rising energy and food costs.
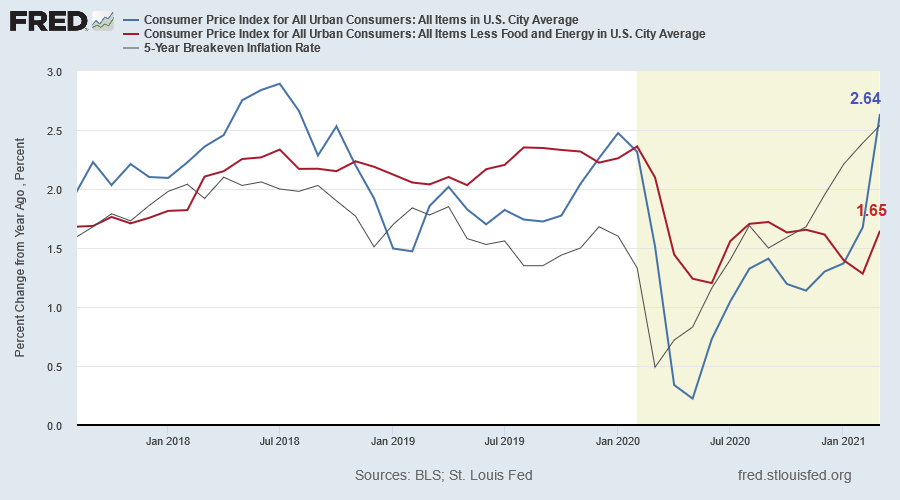
The annual inflation rate in the US ......is the highest reading since August of 2018 with main upward pressure coming from energy (13.2% vs 3.7% in February), namely gasoline (22.5% vs 1.6%), electricity (2.5% vs 2.3%) and utility gas service (9.8% vs 6.7%). Prices also accelerated for used cars and trucks (9.4% vs 9.3%), shelter (1.7% vs 1.5%) and new vehicles (1.5% vs 1.2%) while inflation slowed for medical care services (2.7% vs 3%) and food (3.5% vs 3.6%). Cost of apparel continued to fall (-2.5% vs -3.6%)........a jump in commodities and material costs, coupled with supply constraints, are pushing producer prices up and some companies are passing those costs to clients. (Reuters)
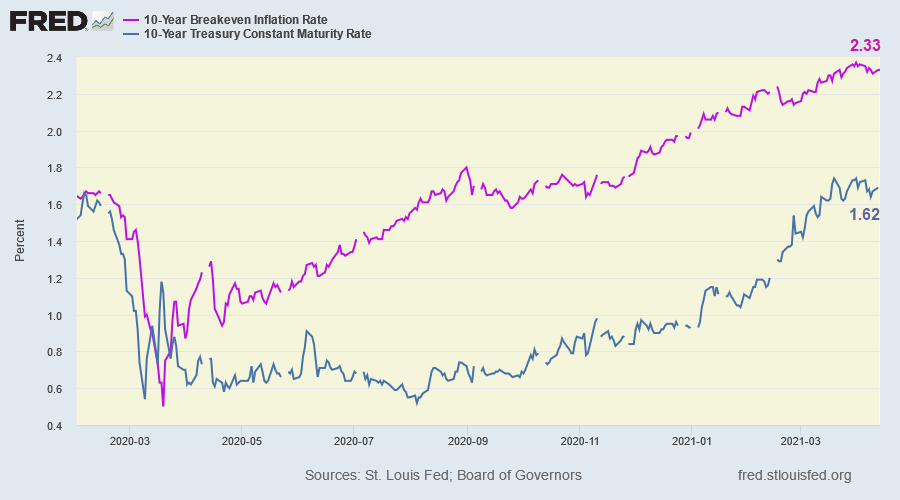
10-year Treasury yields eased to 1.62% with the breakeven inflation rate at 2.33% -- weakening the real 10-year yield to -0.71%.
Inflation and the Money Supply
Milton Friedman famously said, ”Inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon in the sense that it is and can be produced only by a more rapid increase in the quantity of money than in output.“
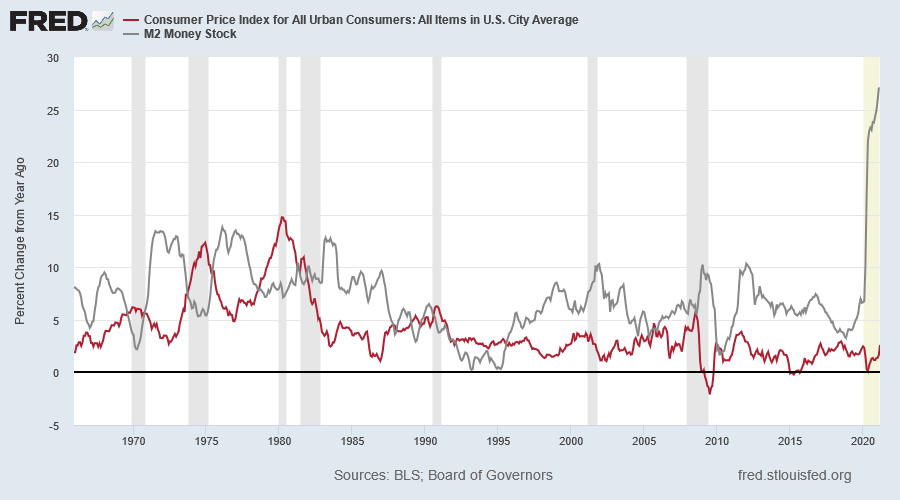
But experience since the 1980s shows several surges in money supply growth without a corresponding rise in inflation. While an increase in money supply may be a prerequisite for a spike in inflation, it is not the cause.
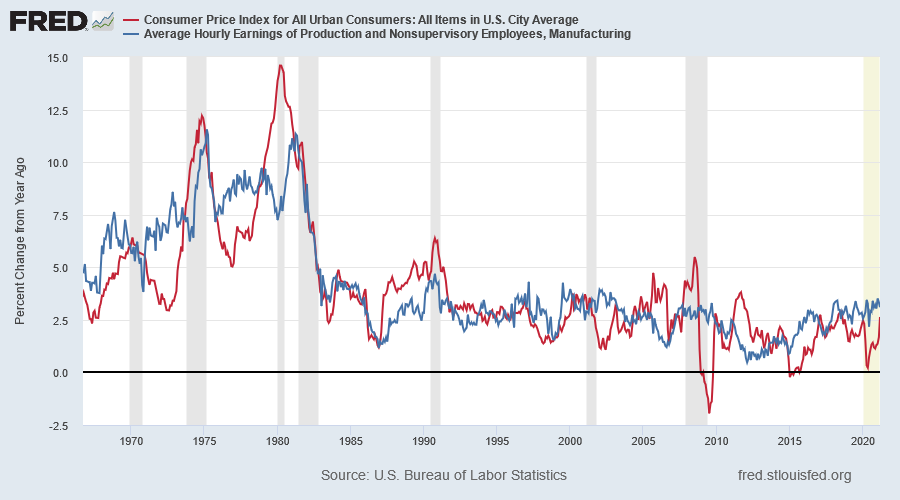
More direct causes of inflation are increases in input costs for suppliers of goods and services. The two largest input costs are commodities and wages. Rises in commodity prices will mostly affect the manufacturing sector, while increases in wage rates impacts on all employers. Also, commodity prices tend to be cyclical, so price fluctuations will be more readily absorbed, while wage increases tend to be permanent and more likely to be passed on to customers.
The chart below shows a much closer correlation between hourly wage rates and CPI since the 1970s, with surges in hourly earnings accompanied by a rise in inflation.
Conclusion
Rising commodity prices are driving higher inflation at present. While some of the pressures may be transitory, due to supply interruptions, underinvestment in new production over the last decade is likely to act as a supply constraint for both energy and base metals. Rising demand fueled by short-term stimulus and longer-term infrastructure investment would act as an accelerant.
Wage rate increases are so far restrained, but that is likely to change as the economy recovers, boosted by decoupling from China and on-shoring of critical supply chains. Shortages of skilled labor are expected to drive up wage rates, maintaining upward pressure on inflation in the longer-term. Training and education of suitable staff will take time.
We have all the ingredients for an inflation spike. A massive boost in the money supply, accompanied by record stimulus payments, much of which has been channeled into savings. This will help to fuel increased demand in the longer term, while restricted supply will drive up commodity prices and wage rates for skilled labor.
Quote for the Week
Unexpected increases in inflation are the de facto equivalent of outright default, for inflation allows all debtors (including the government) to repay their debts in currency that has much less purchasing power than it did when the loans were made.
~ Carmen M. Reinhart, This Time Is Different: Eight Centuries of Financial Folly
Updates for Market Analysis Subscribers
Please take advantage of our $1 special offer for the first month. Cancel at any time.
Disclaimer
Colin Twiggs is director of The Patient Investor Pty Ltd, an Authorised Representative (no. 1256439) of MoneySherpa Pty Limited which holds Australian Financial Services Licence No. 451289.
Everything contained in this web site, related newsletters, training videos and training courses (collectively referred to as the "Material") has been written for the purpose of teaching analysis, trading and investment techniques. The Material neither purports to be, nor is it intended to be, advice to trade or to invest in any financial instrument, or class of financial instruments, or to use any particular methods of trading or investing.
Advice in the Material is provided for the general information of readers and viewers (collectively referred to as "Readers") and does not have regard to any particular person's investment objectives, financial situation or needs. Accordingly, no Reader should act on the basis of any information in the Material without properly considering its applicability to their financial circumstances. If not properly qualified to do this for themselves, Readers should seek professional advice.
Investing and trading involves risk of loss. Past results are not necessarily indicative of future results.
The decision to invest or trade is for the Reader alone. We expressly disclaim all and any liability to any person, with respect of anything, and of the consequences of anything, done or omitted to be done by any such person in reliance upon the whole or any part of the Material.
Please read the Financial Services Guide.

Author: Colin Twiggs is a former investment banker with almost 40 years of experience in financial markets. He co-founded Incredible Charts and writes the popular Trading Diary and Patient Investor newsletters.
Using a top-down approach, Colin identifies key macro trends in the global economy before evaluating selected opportunities using a combination of fundamental and technical analysis.
Focusing on interest rates and financial market liquidity as primary drivers of the economic cycle, he warned of the 2008/2009 and 2020 bear markets well ahead of actual events.
He founded PVT Capital (AFSL No. 546090) in May 2023, which offers investment strategy and advice to wholesale clients.
