What Australia needs is lower land prices
By Colin Twiggs
March 16th, 2013 12:30 a.m. ET (2:30 p:m AET)
These extracts from my trading diary are for educational purposes. Any advice contained therein is provided for the general information of readers and does not have regard to any particular person's investment objectives, financial situation or needs and must not be construed as advice to buy, sell, hold or otherwise deal with any securities or other investments. Accordingly, no reader should act on the basis of any information contained therein without first having consulted a suitably qualified financial advisor. Full terms and conditions can be found at Terms of Use.
Australia enjoyed a mining boom over the last decade but now faces a fall-off in capital expenditure on new projects as commodity prices fall. The RBA, eyeing the coming slow-down with some trepidation, is hoping that housing construction recovers to fill the void. So far the housing market has failed to respond to lower interest rates.
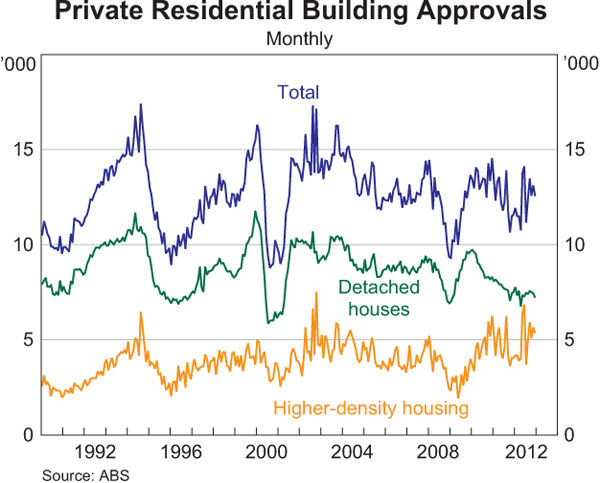
Failure to respond is partly attributable to housing affordability, with household debt in the last 20 years having trebled as a ratio to disposable income.
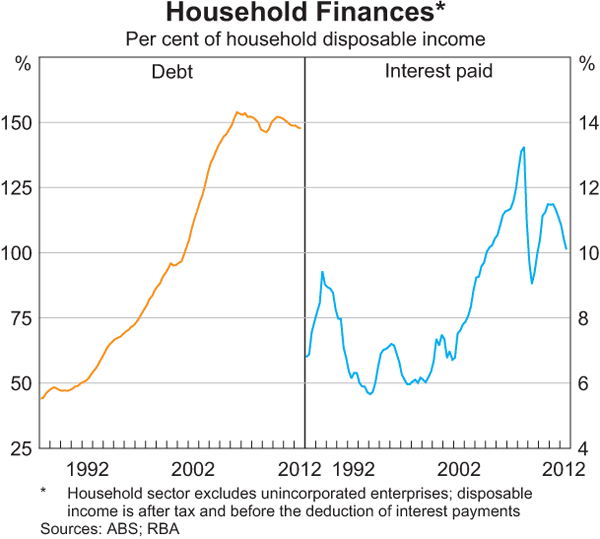
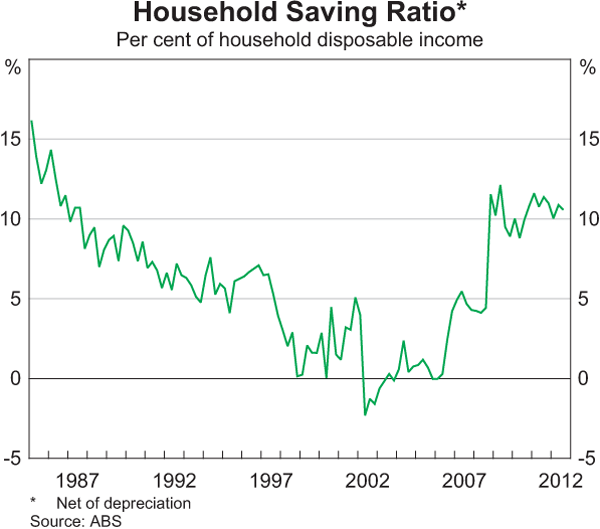
An uncertain financial climate has also contributed, with households more focused on repaying existing debt than on upgrading their homes.
Further cuts in interest rates will not help. Encouraging home buyers to enter the market at unsustainably low interest rates would exacerbate the housing bubble and cause further hardship when rates rise. Rather than monetary policy, we need changes at federal, state and local government level to increase the availability of land for housing.
- Abolish transfer duties
Abolishing transfer duties on property would encourage home-owners to re-size as their needs change, releasing more housing stock into the market. Abolishing transfer duties would also remove state support for higher property prices. Under a transfer duty, higher prices boost state revenues, encouraging support for property developers who land-bank large tracts of land and restrict their release to maintain high prices. - Replace with a land tax
Replacing transfer duties with a land tax, based on the value of the land, would also discourage land-banking by property developers. Restricted release of land is the primary cause of unaffordable housing in both Australia and the UK. - Overcome zoning issues
Zoning issues at state and regional level may also contribute to the slow release of new land for development. - Reduce infrastructure costs
Costs of new infrastructure development are another reason local government tends to restrict release of new land for housing development. Establishment of municipal utility districts ("MUDs") within a local government area would help to overcome this. Leith van Onselen describes how MUDs in Texas, ranging in size from 200 to 5000 hectares, charge home-buyers a monthly infrastructure levy rather than requiring up-front payment for establishment of new services — which raises the purchase price. The MUD levy expires when bonds used to finance the services have been amortized, or residents can decide to continue the levy to upgrade public amenities such as parks, swimming pools and other facilities.
Increased availability of land would drive down new house prices and encourage the establishment of new households. This would boost not only housing construction, building materials and general construction — through establishment of roads and services — but the retail sector as well, because every new home needs to be furnished. New jobs in these sectors would lift general consumption and the broader economy, helping Australia to avoid the approaching mining cliff.
More....
In the economic sphere an act, a habit, an institution, a law produces not only one effect, but a series of effects. Of these effects, the first alone is immediate; it appears simultaneously with its cause; it is seen. The other effects emerge only subsequently; they are not seen; we are fortunate if we foresee them. There is only one difference between a bad economist and a good one: the bad economist confines himself to the visible effect; the good economist takes into account both the effect that can be seen and those effects that must be foreseen.
~ Frederic Bastiat (1848)
